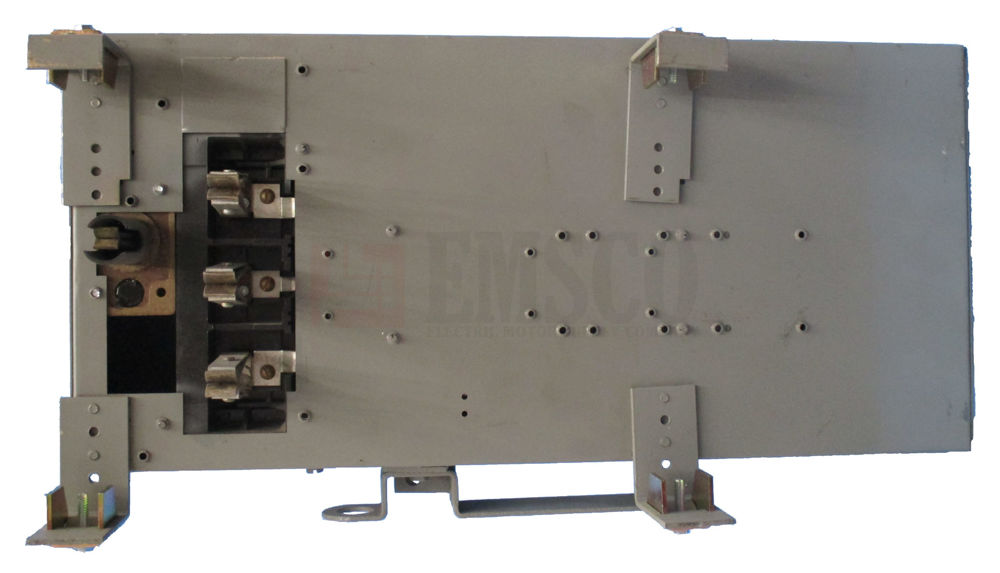
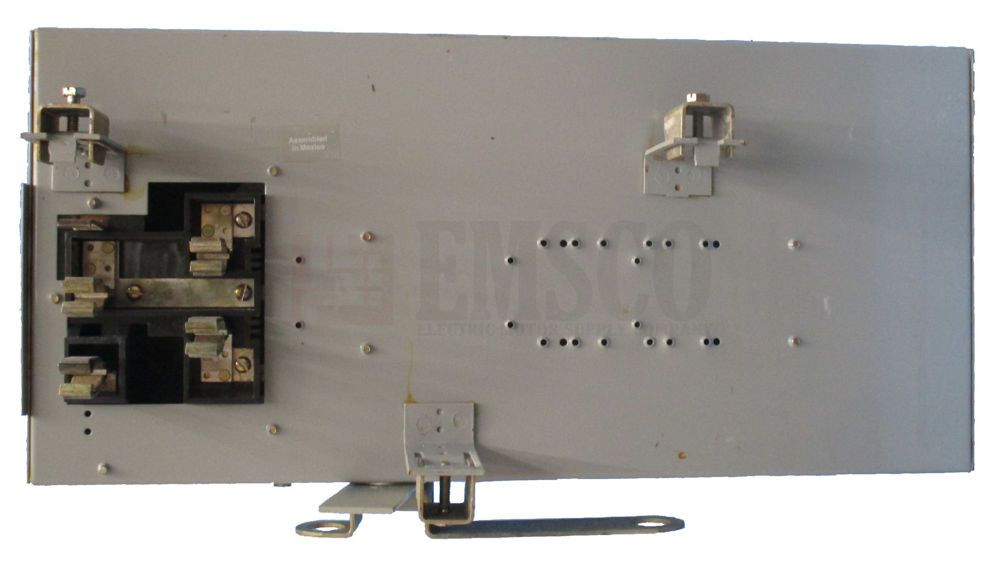
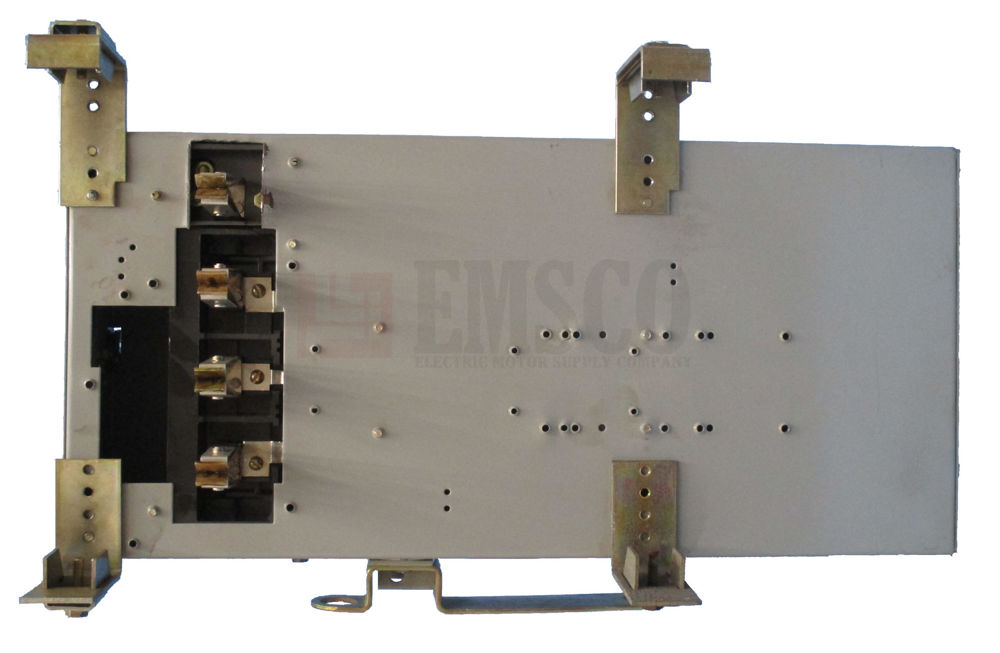
Maximize Efficiency and Savings with Bulldog Busway and Bus Plugs: New, Reconditioned, and Safety-Tested Solutions
Tuesday, June 11, 2024

Upgrading or replacing your existing busway and bus plugs with Bulldog Busway and Bus Plugs—whether new, reconditioned, or used — brings benefits to your facility.
Reconditioned used or inspected and safety-tested Bulldog bus plugs can significantly lower your investment compared to purchasing new ones. These options provide the reliability and efficiency of new equipment at a fraction of the cost, allowing you to allocate budget to other critical areas of your operations.
Bus Plug Testing and Quality Assurance:
EMSCO Reconditioned used and inspected, safety-tested bus plugs undergo testing processes to meet industry standards and your specific operational requirements. This means you can trust that these components will perform reliably, maintaining the safety and integrity of your electrical system.
Bulldog Bus Plugs In Stock for Reduced Lead Times:
Used and reconditioned Bulldog Busway and Bus Plugs are often more readily available than new ones, which can have long lead times due to manufacturing processes and supply chain delays. This means you can upgrade your busway system faster, minimizing disruptions and keep your business moving.
Buyers Checklist Questions for ITE/Siemens Bulldog Bus Plugs
☑️ Amperage
Knowing the available amperage for bus plug options ensures you choose a bus plug that can handle your specific electrical load, preventing overloading and ensuring efficient operation. Selecting the correct amperage rating matching the bus plug's capacity to your system's leads to safety and optimal performance.
☑️ Ground
Review the grounding options provided by ITE Bulldog Bus Plugs. Proper grounding options are essential for electrical safety and system stability, preventing potential hazards and ensuring compliance with safety standards.
☑️ Fusible or Breaker Style Bus Plugs
Choose between fusible and breaker style: Fusible Bus Plugs are ideal for applications where cost is a primary concern, and where high fault current handling capability is needed. Breaker Style Bus Plugs are better suited for applications where minimizing downtime is critical, and where power options are important.
☑️ Voltage
Correct voltage ratings to ensure that the bus plug can handle the electrical potential of your system, preventing mismatches that could lead to equipment failure or safety issues.
☑️ Bus Plug Wiring
Wire compatibility ensures that the bus plug can be securely and effectively connected to your existing wiring, which is critical for maintaining system integrity and performance. This also reduces the risk of faults and improves overall system performance.
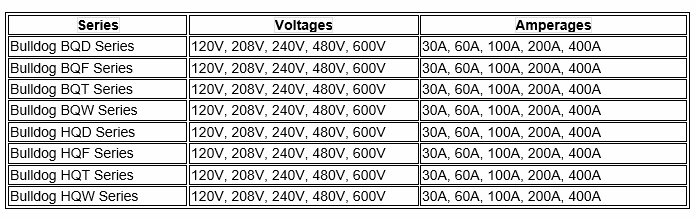
ITE/SIEMENS Bulldog Series Busway Voltage and Amperage
5 Questions to Ask When Choosing Bus Plug Replacements
1. What factors should I consider when selecting the amperage rating for my bus plugs?
Answer:
When deciding on an amperage rating for your bus plugs, keep in mind your system's electrical load requirements, the maximum current the bus plug can carry, and the possibility of future extension. Using the proper amperage rating reduces overloading, improves safety, and extends the life of your electrical components.
2. Should I choose fusible or breaker style bus plugs for my system?
Answer:
Your special needs will determine whether you use fusible or breaker style bus plugs. Fusible bus plugs are inexpensive and can take greater fault currents, but they require fuse replacement after usage. Breaker style bus plugs are resettable and have customizable trip settings, which reduces downtime and increases operating flexibility; still, they are often more expensive upfront.
3. How important is proper grounding for bus plugs, and what options are available?
Answer:
Correct grounding is necessary for electrical safety and system performance. It protects against electrical faults and surges, lowering the risk of equipment damage and providing compliance to safety regulations. To maintain a safe and stable electrical environment, be sure that the bus plugs you purchase have sufficient grounding options that meet the requirements of your system.
4. What voltage ratings should I consider when selecting bus plugs for my electrical system?
Answer:
Check your electrical system's voltage needs for safe compatibility with bus plugs. To guarantee safe and efficient operation, the bus plug's voltage rating must be equal to or greater than the system operating voltage. Common voltage ratings include 120V, 208V, 240V, 480V, and 600V. To avoid malfunctions or safety issues, check whether the bus plugs you choose are capable of handling the voltage in your system.
5. Are there benefits to using reconditioned or inspected and safety-tested bus plugs compared to new ones?
Answer:
These options can provide significant cost savings while still offering reliability and performance equivalent to new components. Reconditioned bus plugs undergo thorough testing to make certain they meet industry standards, making them a practical and economical choice for maintaining and upgrading your electrical system.
Request help online or call a product specialist at 800-328-1842.
Reconditioned, used busway and bus plugs that are inspected and safety tested offer a viable option for your electrical needs. These products go through our evaluation and testing processes to certify they meet safety standards for safety and performance.






